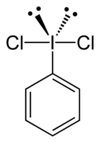
Iodobenzene dichloride
|
|
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
(Dichloro-λ3-iodanyl)benzene
|
|||
| Other names
Iodosobenzene dichloride; Phenyliodine(III) dichloride; Phenyliodo dichloride; Phenyliodoso chloride; Phenylchloroiodonium chloride; Dichloroiodobenzene; Iododichlorobenzene
|
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| Abbreviations | IBD | ||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| C6H5Cl2I | |||
| Molar mass | 274.91 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Yellow solid | ||
| Density | 2.2 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 115 to 120 °C (239 to 248 °F; 388 to 393 K) (decomposes) | ||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
Iodobenzene dichloride (PhICl2) is a complex of iodobenzene with chlorine. As a reagent for organic chemistry, it is used as an oxidant and chlorinating agent.
Single-crystal X-ray crystallography has been used to determine its structure; as can be predicted by VSEPR theory, it adopts a T-shaped geometry about the central iodine atom.
Iodobenzene dichloride is not stable, and is not commonly available commercially. It is prepared by passing chlorine gas through a solution of iodobenzene in chloroform, from which it precipitates. The same reaction has been reported at pilot plant scale (20 kg) as well.
An alternate preparation involving the use of chlorine generated in situ by the action of sodium hypochlorite on hydrochloric acid has also been described.
Iodobenzene dichloride is hydrolyzed by basic solutions to give iodosobenzene (PhIO), and is oxidized by sodium hypochlorite to give iodoxybenzene (PhIO2).
In organic synthesis, iodobenzene dichloride is used as a reagent for the selective chlorination of alkenes and alkynes.
...
Wikipedia