Iodine 123
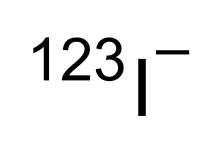 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | 123I− |
| Molar mass | 122.91 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
Iodine-123 (123I or I-123) is a radioactive isotope of iodine used in nuclear medicine imaging, including single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and X-ray computed tomography (X-Ray CT) scans. The isotope's half-life is 13.22 hours; the decay by electron capture to tellurium-123 emits gamma radiation with a predominant energy of 159 keV (this is the gamma primarily used for imaging). In medical applications, the radiation is detected by a gamma camera. The isotope is typically applied as iodide-123, the anionic form.
Iodine-123 is produced in a cyclotron by proton irradiation of xenon in a capsule. Xenon-124 absorbs a proton and immediately loses a neutron and proton to form xenon-123, or else loses two neutrons to form caesium-123, which decays to xenon-123. The xenon-123 formed by either route then decays to iodine-123, and is collected on the side of the capsule under refrigeration, then eluted with dilute sodium hydroxide in a halogen disproportionation reaction, similar to collection of iodine-125 after it is formed from xenon by neutron irradiation (see that article for more).
Iodine-123 is usually supplied as the iodide and hypoiodite (OI−) in dilute sodium hydroxide solution, at high isotopic purity.
I-123 for medical applications has also been produced at Oak Ridge National Laboratories by proton cyclotron bombardment of 80% isotopically enriched tellurium-123.
...
Wikipedia
