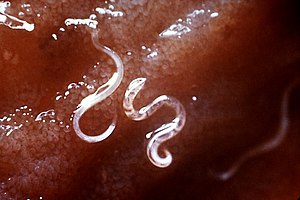
Hookworm
| Hookworm infection | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Hookworms | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
| ICD-10 | B76.8 |
| ICD-9-CM | 126.9 |
Hookworm infection, also known as hookworm disease, is an infection by a parasitic bloodsucking roundworm. Hookworm infections include ancylostomiasis and necatoriasis. These worms live in the small intestine which may be that of a bird or mammal such as a dog, cat, or human. Hookworm infection in pregnancy can cause poor growth, premature birth and a low birth weight of the baby. Hookworms in children can cause intellectual and growth problems.
Two species of hookworms commonly infect humans: Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus. A. duodenale is the more common type in the Middle East, North Africa, India and (formerly) in southern Europe, while N. americanus is the more common type in the Americas, Sub-Saharan Africa, Southeast Asia, China, and Indonesia. A. tubaeforme infects cats, A. caninum infects dogs and A. braziliense and Uncinaria stenocephala infect both cats and dogs. Hookworms are much smaller than the giant roundworms Ascaris lumbricoides. The most significant risk of hookworm infection is anemia, secondary to loss of iron (and protein) in the gut. The worms suck blood and damage the mucosa. However, the blood loss in the stools is not visibly apparent.
...
Wikipedia
