Halifax County, Virginia
| Halifax County, Virginia | ||
|---|---|---|

Halifax County Courthouse in April 2014
|
||
|
||
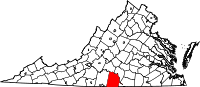 Location in the U.S. state of Virginia |
||
 Virginia's location in the U.S. |
||
| Founded | 1752 | |
| Named for | George Montague-Dunk, 2nd Earl of Halifax | |
| Seat | Halifax | |
| Largest town | South Boston | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 830 sq mi (2,150 km2) | |
| • Land | 818 sq mi (2,119 km2) | |
| • Water | 12 sq mi (31 km2), 1.4% | |
| Population (est.) | ||
| • (2015) | 35,125 | |
| • Density | 42/sq mi (16/km²) | |
| Congressional district | 5th | |
| Time zone | Eastern: UTC-5/-4 | |
| Website | www |
|
Halifax County is a county located in the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2010 census, the population was 36,241. Its county seat is Halifax.
Occupied by varying cultures of indigenous peoples for thousands of years, in historic times English colonists encountered Siouan-speaking Native Americans. Halifax County was established in 1752 by English colonists from Lunenburg County. The county was named for George Montague-Dunk, 2nd Earl of Halifax.
Through the 1990 Census, the City of South Boston in Halifax County was a separate county. South Boston became a town again and rejoined Halifax County on July 1, 1995.
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 830 square miles (2,100 km2), of which 818 square miles (2,120 km2) is land and 12 square miles (31 km2) (1.4%) is water.
As of the census of 2000, there were 37,355 people, 15,018 households, and 10,512 families residing in the county. The population density was 46 people per square mile (18/km²). There were 16,953 housing units at an average density of 21 per square mile (8/km²). The racial makeup of the county was 60.32% White, 38.02% Black or African American, 0.20% Native American, 0.24% Asian, 0.01% Pacific Islander, 0.44% from other races, and 0.77% from two or more races. 1.23% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race.
...
Wikipedia

