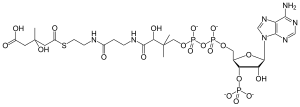
HMG-CoA
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
(9R,21S)-1-[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-
(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy- 3-(phosphonooxy)tetrahydrofuran-2-yl]- 3,5,9,21-tetrahydroxy-8,8,21-trimethyl- 10,14,19-trioxo-2,4,6-trioxa-18-thia- 11,15-diaza-3,5-diphosphatricosan-23- oic acid 3,5-dioxide |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.014.820 |
| MeSH | HMG-CoA |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C27H44N7O20P3S | |
| Molar mass | 911.661 g/mol |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy- 3-(phosphonooxy)tetrahydrofuran-2-yl]- 3,5,9,21-tetrahydroxy-8,8,21-trimethyl- 10,14,19-trioxo-2,4,6-trioxa-18-thia- 11,15-diaza-3,5-diphosphatricosan-23-
HMG-CoA (or 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A) is an intermediate in the mevalonate and ketogenesis pathways. It is formed from acetyl CoA and acetoacetyl CoA by HMG-CoA synthase. The researches of Minor J. Coon and Bimal Kumar Bachhawat in the 1950s at University of Illinois led to its discovery.
It is also an intermediate in the metabolism of leucine. Its immediate precursor is 3-methylglutaconyl CoA.
HMG-CoA reductase converts it into mevalonic acid.
HMG-CoA lyase breaks it into acetyl CoA and acetoacetate.
...
Wikipedia
