Griseofulvin
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Gris-peg, Grifulvin V, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682295 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
by mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Highly variable (25 to 70%) |
| Metabolism | liver (demethylation and glucuronidation) |
| Biological half-life | 9–21 hours |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.335 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
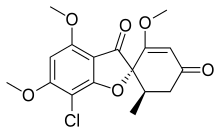
| Formula | C17H17ClO6 |
| Molar mass | 352.766 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
Griseofulvin is antifungal medication used to treat a number of types of dermatophytoses (ringworm). This includes fungal infections of the nails and skin when antifungal creams have not worked. It is taken by mouth.
Common side effects include allergic reactions, nausea, diarrhea, headache, trouble sleeping, and feeling tired. It is not recommended in people with liver failure or porphyria. Use during or in the months before pregnancy may result in harm to the baby. Griseofulvin works by interfering with fungal mitosis.
Griseofulvin was discovered in 1939 from a type of Penicillium mold. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system. The wholesale cost in the developing world is about 0.05 to 0.18 USD per day. In the United States a course of treatment costs 100 to 200 USD.
Griseofulvin is used orally only for dermatophytosis. It is ineffective topically. It is reserved for cases with nail, hair, or large body surface involvement.
Known side effects of griseofulvin include:
The drug binds to tubulin, interfering with microtubule function, thus inhibiting mitosis. It binds to keratin in keratin precursor cells and makes them resistant to fungal infections. The drug reaches its site of action only when hair or skin is replaced by the keratin-griseofulvin complex. Griseofulvin then enters the dermatophyte through energy-dependent transport processes and bind to fungal microtubules. This alters the processing for mitosis and also underlying information for deposition of fungal cell walls.
...
Wikipedia
