Great Bear Lake
| Great Bear Lake | |
|---|---|
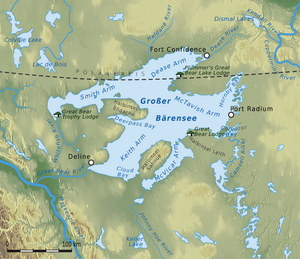
Great Bear Lake, Northwest Territories
|
|
| Location | Northwest Territories |
| Coordinates | 66°N 121°W / 66°N 121°WCoordinates: 66°N 121°W / 66°N 121°W |
| Primary outflows | Great Bear River |
| Catchment area | 114,717 km2 (44,292 sq mi) |
| Basin countries | Canada |
| Surface area | 31,153 km2 (12,028 sq mi) |
| Average depth | 71.7 m (235 ft) |
| Max. depth | 446 m (1,463 ft) |
| Water volume | 2,236 km3 (536 cu mi) |
| Residence time | 124 years |
| Shore length1 | 2,719 km (1,690 mi) (plus 824 km (512 mi) island shoreline) |
| Surface elevation | 156 m (512 ft) |
| Frozen | November - July |
| Islands | 26 main islands, totaling 759.3 km2 (293.2 sq mi) in area |
| Settlements | Deline |
| References | |
| 1 Shore length is not a well-defined measure. | |
The Great Bear Lake (Slavey: Sahtú /ˈsɑː.tuː/, French: Grand lac de l'Ours) is the largest lake entirely in Canada (Lake Superior and Lake Huron straddling the Canada-US border are larger), the fourth largest in North America, and the eighth largest in the world. The lake is in the Northwest Territories, on the Arctic Circle between 65 and 67 degrees of northern latitude and between 118 and 123 degrees western longitude, 156 m (512 ft) above sea level.
The name originated from the words "Satudene" in Denesuline meaning “grizzly bear water people.” The Sahtu Dene people are named after the lake. Grizzly Bear Mountain on the shore of the lake also comes from Denesuline, meaning, “bear large hill.”
The Sahoyue (Grizzly Bear Mountain) peninsula on the south side of the lake and the Edacho (Scented Grass Hills) peninsula on the west side form the Saoyú-ʔehdacho National Historic Site of Canada.
...
Wikipedia
