Gralise
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Neurontin, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a694007 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 27–60% (inversely proportional to dose; a high fat meal also increases bioavailability) |
| Protein binding | Less than 3% |
| Metabolism | Not significantly metabolised |
| Biological half-life | 5 to 7 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.056.415 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
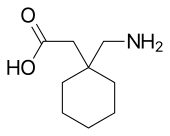
| Formula | C9H17NO2 |
| Molar mass | 171.237 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
Gabapentin (GPN), marketed under the brand name Neurontin among others, is a medication used to treat epilepsy, neuropathic pain, hot flashes, and restless leg syndrome. In epilepsy it may be used for those with partial seizures. It is recommended as one of a number of first line medications for the treatment of neuropathic pain in diabetic neuropathy, post-herpetic neuralgia, and central neuropathic pain. A 2014 review of its use for diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia found that about 14% of people have a meaningful benefit.
Common side effects include sleepiness and dizziness. Serious side effects may include an increased risk of suicide, aggressive behaviour, and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms. It is unclear if it is safe during pregnancy or breastfeeding. Lower doses should be used in people with kidney problems. Gabapentin affects the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) but how it works is otherwise unclear.
Gabapentin was first approved for use in 1993. The wholesale price in the developing world is about US$40.50 per month. In the United States it has been available as a generic medication since 2004. As of 2015 the cost for a typical month of medication in the United States is US$100 to US$200. During the 1990s Parke-Davis, a sub-company of Pfizer, used a number of techniques to encourage physicians in the United States to use gabapentin for unapproved uses.
...
Wikipedia
