Gonorrhoea
| Gonorrhea | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | gonococcal infection, gonococcal urethritis, gonorrhoea, the clap |
 |
|
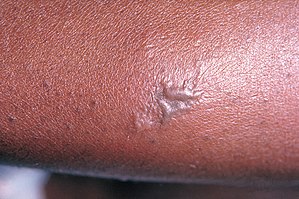
| Gonococcal lesion on the skin | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
| ICD-10 | A54 |
| ICD-9-CM | 098 |
| DiseasesDB | 8834 |
| MedlinePlus | 007267 |
| eMedicine | article/782913 |
| Patient UK | Gonorrhea |
| MeSH | D006069 |
Gonorrhea, also spelled gonorrhoea, is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Many people have no symptoms. Men may have burning with urination, discharge from the penis, or testicular pain. Women may have burning with urination, vaginal discharge, vaginal bleeding between periods, or pelvic pain. Complications in women include pelvic inflammatory disease and in men include inflammation of the epididymis. If untreated gonorrhea can occasionally spread to affect joints or heart valves.
Gonorrhea is spread through sexual contact with an infected person. This includes oral, anal, and vaginal sex. It can also spread from a mother to a child during birth. Diagnosis is by testing the urine, urethra in males, or cervix in females. Testing all women who are sexually active and less than 25 years of age each year as well as those with new sexual partners is recommended. This same recommendation applies in men who have sex with men.
Gonorrhea can be prevented with the use of condoms, having sex with only one person who is uninfected, and by not having sex. Treatment is usually with ceftriaxone by injection and azithromycin by mouth. Resistance has developed to many previously used antibiotics and higher doses of ceftriaxone are occasionally required. Retesting is recommended three months after treatment. Sexual partners from the last 2 months should also be treated.
...
Wikipedia
