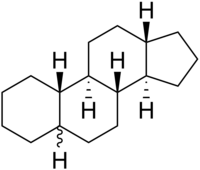
Gonane
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
2(8S,9R,10S,13S,14R)-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
|
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C17H28 | |
| Molar mass | 232.41 g·mol−1 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Gonane (C17), also known as perhydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthrene, is a tetracyclic hydrocarbon ring structure and the fundamental steroid nucleus. It consists of a phenanthrene ring fused with a cyclopentane ring. Unlike steroid hormones, gonane has no methyl groups at the C10 and C13 positions and no side chain at the C17 position. Because gonane has six centers of chirality, it has 64 (26) theoretically possible stereoisomers. However, only a few of these stereoisomers are actually encountered with steroids. The most common stereoisomers of gonane are 5α-gonane and 5β-gonane.
5α-Gonane
5β-Gonane
5α-Gonane, side-perspective view
5β-Gonane, side-perspective view
Estrane (C18) is the 13β-methyl variant of gonane, androstane (C19) is the 10β,13β-dimethyl variant of gonane, and pregnane (C21) is the 10β,13β-dimethyl, 17β-ethyl variant of gonane.
...
Wikipedia
