Golgi complex
| Cell biology | |
|---|---|
| The animal cell | |
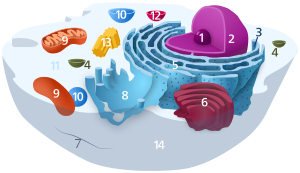
Components of a typical animal cell:
|
The Golgi apparatus (/ˈɡoʊldʒiː/), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. It was identified in 1897 by the Italian scientist Camillo Golgi and named after him in 1898.
Part of the cellular endomembrane system, the Golgi apparatus packages proteins into membrane-bound vesicles inside the cell before the vesicles are sent to their destination. The Golgi apparatus resides at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. It is of particular importance in processing proteins for secretion, containing a set of glycosylation enzymes that attach various sugar monomers to proteins as the proteins move through the apparatus.
Owing to its large size and distinctive structure, the Golgi apparatus was one of the first organelles to be discovered and observed in detail. It was discovered in 1898 by Italian physician Camillo Golgi during an investigation of the nervous system. After first observing it under his microscope, he termed the structure the internal reticular apparatus. Some doubted the discovery at first, arguing that the appearance of the structure was merely an optical illusion created by the observation technique used by Golgi. With the development of modern microscopes in the 20th century, the discovery was confirmed. Early references to the Golgi referred to it by various names including the "Golgi–Holmgren apparatus", "Golgi–Holmgren ducts", and "Golgi–Kopsch apparatus". The term "Golgi apparatus" was used in 1910 and first appeared in the scientific literature in 1913.
...
Wikipedia
