Gluconate
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
D-Gluconic acid
|
|
| Other names
Dextronic acid
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
526-95-4 133-42-6 (racemate) |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:33198 |
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL464345 |
| ChemSpider |
10240 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.639 |
| EC Number | 208-401-4 |
| E number | E574 (acidity regulators, ...) |
| PubChem | 10690 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C6H12O7 | |
| Molar mass | 196.16 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless crystals |
| Melting point | 131 °C (268 °F; 404 K) |
| Good | |
| Acidity (pKa) | 3.86 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
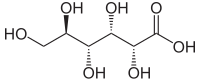
Gluconic acid is an organic compound with molecular formula C6H12O7 and condensed structural formula HOCH2(CHOH)4COOH. It is one of the 16 stereoisomers of 2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanoic acid.
In aqueous solution at neutral pH, gluconic acid forms the gluconate ion. The salts of gluconic acid are known as "gluconates". Gluconic acid, gluconate salts, and gluconate esters occur widely in nature because such species arise from the oxidation of glucose. Some drugs are injected in the form of gluconates.
The chemical structure of gluconic acid consists of a six-carbon chain with five hydroxyl groups terminating in a carboxylic acid group. In aqueous solution, gluconic acid exists in equilibrium with the cyclic ester glucono delta-lactone.
Gluconic acid occurs naturally in fruit, honey, and wine. As a food additive (E574), it is an acidity regulator. It is also used in cleaning products where it dissolves mineral deposits especially in alkaline solution. The gluconate anion chelates Ca2+, Fe2+, Al3+, and other metals. In 1929 Horace Terhune Herrick developed a process for producing the salt by fermentation.
...
Wikipedia
