Germinal center
| Germinal center | |
|---|---|
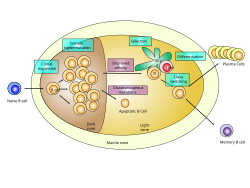
Germinal center of a lymph node showing proliferation and development stages of a B cell .
|
|
| Dorlands /Elsevier |
c_20/12226657 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
Germinal centers or germinal centres (GCs) are sites within lymph nodes (secondary lymphoid organs) where mature B cells proliferate, differentiate, and mutate their antibody genes (through somatic hypermutation), and switch the class of their antibodies (for example from IgM to IgG) during a normal immune response to an infection. They develop dynamically after the activation of follicular B cells by T-dependent antigen.
As they undergo rapid and mutative cellular division in the dark zone, B cells of the germinal center are known as centroblasts. Once these B cells have stopped proliferating, they migrate to the light zone where they are known as centrocytes, and are subjected to selection by follicular helper T (TFH) cells in the presence of follicular dendritic cells (FDCs). Germinal centers are an important part of the B cell humoral immune response, acting as central factories for the generation of affinity matured B cells specialized in producing improved antibodies that effectively recognize infectious agents, and for the production of durable memory B cells. Histologically, the GCs describe microscopically distinguishable parts in lymphoid tissues.
The morphology of GCs is very specific and shows properties which are characteristic for different stages of the reaction.
...
Wikipedia
