Gelatinous drop-like corneal dystrophy
| Gelatinous drop-like corneal dystrophy | |
|---|---|
 |
|
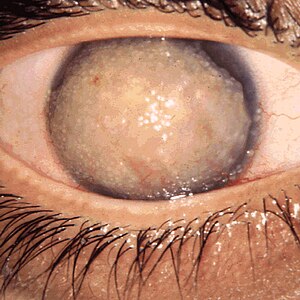
| A completely opaque cornea with multiple drop-like nodular opacities. Some blood vessels are present in the opaque cornea | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| OMIM | 204870 |
Gelatinous drop-like corneal dystrophy, also known as amyloid corneal dystrophy, is a rare form of corneal dystrophy. The disease was described by Nakaizumi as early as 1914.
A number of mutations causing this disease have been described in the M1S1 (TACSTD2) gene encoding Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2, but not all patients have these mutations, suggesting involvement of other genes.
The main pathological features in this dystrophy are mulberry-shaped gelatinous masses beneath the corneal epithelium. Patients suffer from photophobia, foreign body sensation in the cornea. The loss of vision is severe. The amyloid nodules have been found to contain lactoferrin, but the gene encoding lactoferrin is unaffected. Typically the peripheral cornea is spared involvement.
This form of corneal amyloidosis appears to be more frequent in Japan.
Recurrence within a few years occurs in all patients following corneal transplantation. Soft contact lenses are effective in decreasing recurrences.
...
Wikipedia
