Fukuyama congenital muscular dystrophy
| Fukuyama congenital muscular dystrophy | |
|---|---|
 |
|
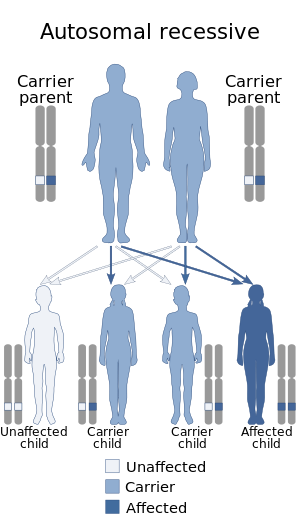
| Fukuyama congenital muscular dystrophy has an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| ICD-10 | G71.2 |
| OMIM | 253800 |
| Orphanet | 272 |
Fukuyama congenital muscular dystrophy (FCMD) is a rare, autosomal recessive form of muscular dystrophy (weakness and breakdown of muscular tissue) mainly described in Japan but also identified in Turkish and Ashkenazi Jewish patients, fifteen cases were first described on 1960 by Fukuyama.
FCMD mainly affects the brain, eyes, and muscles, in particular, the disorder affects development of the skeletal muscles leading to weakness and deformed appearances, and brain development is blunted affecting cognitive functioning as well as social skills. In 1995, the disorder was linked to mutations in a gene coding for the protein fukutin (the FCMD gene). Fukuyama congenital muscular dystrophy is the second most prevalent form of muscular dystrophy in Japan. One out of every 90 people in Japan is a heterozygous carrier.
In terms of the signs/symptoms of Fukuyama congenital muscular dystrophy it is characterized by a decrease in skeletal muscle tone as well as an impairment in brain and eye development.Initial symptoms of FCMD present in early infancy as decreased ability to feed. Marked differences in facial appearance occur due to decreased muscle tone. Further characteristics include:
Fukuyama congenital muscular dystrophy also affects the nervous system and various associated parts. FCMD affects normal development of the brain producing a broadly smooth, bumpy shaped cortex named cobblestone lissencephaly as well as various other malformations, notably micropolygyria. Children also experience delayed myelination in the brain.
The cause of Fukuyama congenital muscular dystrophy is rooted in the FKTN gene, located at human chromosome 9q31, codes for the protein fukutin. Mutations in this gene, and therefore the fukutin protein, are the cause of FCMD. The disease is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner.
...
Wikipedia
