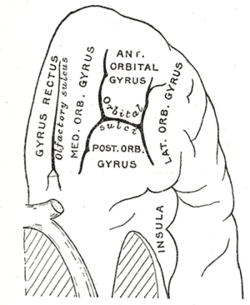
Frontal lobes
| The frontal Lobe | |
|---|---|
|
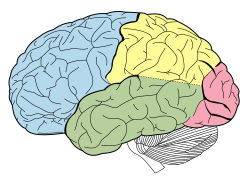
Principal fissures and lobes of the cerebrum viewed laterally. (Frontal lobe is shown in blue.)
|
|
 |
|
| Details | |
| Part of | Cerebrum |
| Artery |
Anterior cerebral Middle cerebral |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Lobus frontalis |
| Acronym(s) | FL |
| MeSH | A08.186.211.730.885.213.270 |
| NeuroNames | hier-37 |
| NeuroLex ID | Frontal Lobe |
| TA | A14.1.09.110 |
| FMA | 61824 |
|
Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
[]
|
|
The frontal lobe, located at the front of the brain, is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the mammalian brain. The frontal lobe is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere and positioned in front of the parietal lobe and above and in front of the temporal lobe. It is separated from the parietal lobe by a space between tissues called the central sulcus, and from the temporal lobe by a deep fold called the lateral sulcus also called the Sylvian fissure. The precentral gyrus, forming the posterior border of the frontal lobe, contains the primary motor cortex, which controls voluntary movements of specific body parts.
The frontal lobe contains most of the dopamine-sensitive neurons in the cerebral cortex. The dopamine system is associated with reward, attention, short-term memory tasks, planning, and motivation. Dopamine tends to limit and select sensory information arriving from the thalamus to the forebrain. A report from the National Institute of Mental Health says a gene variant that reduces dopamine activity in the prefrontal cortex is related to poorer performance and inefficient functioning of that brain region during working memory tasks, and to a slightly increased risk for schizophrenia.
...
Wikipedia