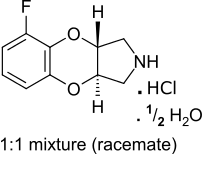
Fluparoxan
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 85% oral from tablet formulation |
| Metabolism | greater than 90% excreted as (sulphamic acid and carbamoyI glucuronide conjugates) |
| Biological half-life | 6 hours |
| Excretion | renal |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| Synonyms | (+/-)-(trans)-5-fluoro-2,3,3a,9a-tetrahydro-1H-[1,4]benzodioxino[2,3-c]pyrrole hydrochloride hemihydrate |
| CAS Number |
|
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H12ClFNO2.5 |
| Molar mass | 240.66 g·mol−1 |
Fluparoxan (GR50360A) (+/-)-(trans)-5-fluoro-2,3,3a,9a-tetrahydro-1H-[1,4]benzodioxino[2,3-c]pyrrole hydrochloride hemihydrate is a potent α2-adrenergic receptor antagonist (pKB = 7.9) with excellent α2/α1 selectivity (2630 fold), and is the only well-studied a2 antagonist in its structural family which does not antagonize any variant of the imidazoline receptor. It was shown to possess central α2-adrenoceptor antagonist activity after oral doses in man and was patented as an antidepressant by Glaxo in the early 1980s, but its development was discontinued when the compound failed to show a clear clinical advantage over existing therapies.
Fluparoxan is a very selective α2-adrenergic blocker, that readily cross the blood–brain barrier. Blockade of α2-adrenoreceptors, particularly presynaptic autoreceptors in noradrenergic neurons by fluparoxan, produces an increase in the synaptic concentrations of noradrenaline, by blocking the autoinhibitory feedback mechanism. This release of noradrenaline has a potential value in the treatment of disorders which are associated with a deficiency of noradrenaline at postsynaptic adrenoreceptors, such as depression, the early features of Alzheimer's disease and schizophrenia and other neurodevelopmental disorders associated with cognitive impairment. Fluparoxan also exhibits no anticholinergic, antidopaminergic, alpha1-adrenergic, beta-adrenergic, muscarinic or 5-HT1-receptor-blocking effects.
Fluparoxan showed α2-adrenoceptors antagonist activity in vivo in several animal species. In the conscious mouse, fluparoxan was effective by the oral route in preventing clonidine-induced hypothermia and antinociception. While in the rat the marked impairment of rotarod performance were prevented dose-dependently by fluparoxan. Fluparoxan, orally prevented agonist UK-14304 induced sedation and bradycardia in a dose-related fashion in the dog. Fluparoxan has been shown to possess central α2-adrenoceptor antagonist activity after both single and repeated oral doses in man, significantly attenuating all responses to the agonist clonidine (growth hormone secretion, bradycardia, hypotension, xerostomia) apart from the measures of sedation.
...
Wikipedia
