Fissure (dentistry)
| Tooth decay | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Dental caries, cavities, caries |
 |
|
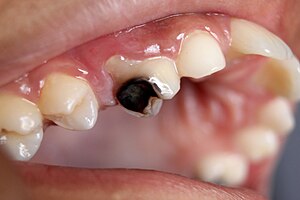
| Destruction of a tooth by dental caries. | |
| Pronunciation |
|
| Specialty | Dentistry |
| Symptoms | Pain, tooth loss, difficulty eating |
| Complications | Inflammation around the tooth, tooth loss, infection or abscess formation |
| Duration | Long term |
| Causes | Bacteria producing acid from food debris |
| Risk factors | Diet high in simple sugar, diabetes mellitus, Sjogren's syndrome, medications that decrease saliva |
| Prevention | Low sugar diet, teeth brushing, fluoride |
| Medication | Paracetamol (acetaminophen), ibuprofen |
| Frequency | 2.3 billion (2015) |
| Classification |
· ·
|
|---|---|
| External resources |
Tooth decay, also known as dental caries or cavities, is a breakdown of teeth due to acids made by bacteria. The cavities may be a number of different colors from yellow to black. Symptoms may include pain and difficulty with eating. Complications may include inflammation of the tissue around the tooth, tooth loss, and infection or abscess formation.
The cause of caries is acid from bacteria dissolving the hard tissues of the teeth (enamel, dentin and cementum). The acid is produced from food debris or sugar on the tooth surface.Simple sugars in food are these bacteria's primary energy source and thus a diet high in simple sugar is a risk factor. If mineral breakdown is greater than build up from sources such as saliva, caries results. Risk factors include conditions that result in less saliva such as: diabetes mellitus, Sjogren's syndrome and some medications. Medications that decrease saliva production include antihistamines and antidepressants. Caries is also associated with poverty, poor cleaning of the mouth, and receding gums resulting in exposure of the roots of the teeth.
Prevention of dental caries includes regular cleaning of the teeth, a diet low in sugar, and small amounts of fluoride. Brushing the teeth twice per day and flossing between the teeth once a day is recommended by many. Fluoride may be from water, salt or toothpaste among other sources. Treating a mother's dental caries may decrease the risk in her children by decreasing the numbers of certain bacteria. Screening can result in earlier detection. Depending on the extent of destruction, various treatments can be used to restore the tooth to proper function or the tooth may be removed. There is no known method to grow back large amounts of tooth. The availability of treatment is often poor in the developing world.Paracetamol (acetaminophen) or ibuprofen may be taken for pain.
...
Wikipedia
