Fabry's disease
| Fabry disease | |
|---|---|
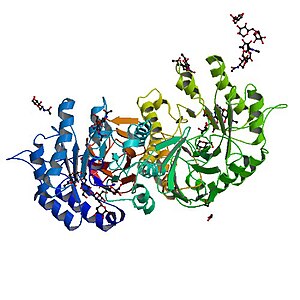 |
|
| Alpha galactosidase - the deficient protein Fabry disease | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | endocrinology |
| ICD-10 | E75.2 (ILDS E75.25) |
| ICD-9-CM | 272.7 |
| OMIM | 301500 |
| DiseasesDB | 4638 |
| eMedicine | neuro/579 derm/707 ped/2888 |
| MeSH | D000795 |
| GeneReviews | |
Fabry disease (/ˈfɑːbri/) (also known as Fabry's disease, Anderson-Fabry disease, angiokeratoma corporis diffusum, and alpha-galactosidase A deficiency) is a rare genetic lysosomal storage disease, inherited in an X-linked manner. Fabry disease can cause a wide range of systemic symptoms. It is a form of sphingolipidosis, as it involves dysfunctional metabolism of sphingolipids. The disease is named after one of its discoverers, Johannes Fabry (June 1, 1860 – June 29, 1930).
Symptoms are typically first experienced in early childhood and can be very difficult to understand; the rarity of Fabry disease to many clinicians sometimes leads to misdiagnoses. Manifestations of the disease usually increase in number and severity as an individual ages.
Full body or localized pain to the extremities (known as acroparesthesia) or gastrointestinal (GI) tract is common in patients with Fabry disease. This acroparesthesia is believed to be related to the damage of peripheral nerve fibers that transmit pain. GI tract pain is likely caused by accumulation of lipids in the small vasculature of the GI tract which obstructs blood flow and causes pain.
Kidney complications are a common and serious effect of the disease; kidney insufficiency and kidney failure may worsen throughout life. The presence of protein in the urine (which causes foamy urine) is often the first sign of kidney involvement. End-stage kidney failure in those with Fabry disease typically occurs in the third decade of life, and is a common cause of death due to the disease.
Cardiac complications occur when glycolipids build up in different heart cells; heart-related effects worsen with age and may lead to increased risk of heart disease. High blood pressure and restrictive cardiomyopathy are commonly observed.
...
Wikipedia
