Lysosomal storage disease
| Lysosomal storage disease | |
|---|---|
 |
|
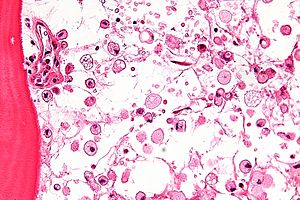
| Micrograph of Gaucher disease, with cells that have the characteristic crumpled tissue paper-like cytoplasm. H&E stain. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | endocrinology |
| ICD-10 | E75-E77 |
| MeSH | D016464 |
Lysosomal storage diseases (LSDs; /ˌlaɪsəˈsoʊməl/) are a group of approximately 50 rare inherited metabolic disorders that result from defects in lysosomal function.Lysosomes are sacs of enzymes within cells that digest large molecules and pass the fragments on to other parts of the cell for recycling. This process requires several critical enzymes. If one of these enzymes is defective, because of a mutation, the large molecules accumulate within the cell, eventually killing it.
Lysosomal storage disorders are caused by lysosomal dysfunction usually as a consequence of deficiency of a single enzyme required for the metabolism of lipids, glycoproteins (sugar containing proteins) or so-called mucopolysaccharides. Individually, LSDs occur with incidences of less than 1:100,000; however, as a group the incidence is about 1:5,000 - 1:10,000. Most of these disorders are autosomal recessively inherited such as Niemann–Pick disease, type C, however a few are X-linked recessively inherited, such as Fabry disease and Hunter syndrome (MPS II).
The lysosome is commonly referred to as the cell's recycling center because it processes unwanted material into substances that the cell can utilize. Lysosomes break down this unwanted matter via enzymes, highly specialized proteins essential for survival. Lysosomal disorders are usually triggered when a particular enzyme exists in too small an amount or is missing altogether. When this happens, substances accumulate in the cell. In other words, when the lysosome does not function normally, excess products destined for breakdown and recycling are stored in the cell.
...
Wikipedia
