Elevated alkaline phosphatase
| Elevated alkaline phosphatase | |
|---|---|
 |
|
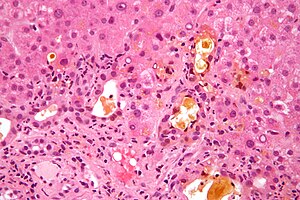
| Micrograph showing changes that may be associated with an elevated alkaline phosphatase (cholestasis and feathery degeneration). Liver biopsy. H&E stain. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Pathology |
| ICD-10 | R74.8 |
| ICD-9-CM | 790.5 |
Elevated alkaline phosphatase describes the situation where the levels of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) exceed the reference range. This group of enzymes has a low substrate specificity and catalyzes the hydrolysis of phosphate esters in a basic environment. The major function of alkaline phosphatase is transporting across cell membranes. Alkaline phosphatases are present in many human tissues, including bone, intestine, kidney, liver, placenta and white blood cells. Damage to these tissues causes the release of ALP into the bloodstream. Elevated levels can be detected through a blood test. Elevated alkaline phosphate is associated with certain medical conditions or syndromes (e.g., hyperphosphatasia with mental retardation syndrome, HPMRS). It serves as a significant indication for certain medical conditions, diseases and syndromes.
If the reason for alkaline phosphatase is unknown, isoenzyme studies using electrophoresis can confirm the source of the ALP. Heat stability also distinguishes bone and liver isoenzymes ("bone burns, liver lasts").
Other unlisted musculoskeletal conditions may also cause elevated alkaline phosphatase.
Elevated levels of the alkaline phosphatase enzyme are reported with those who have obesity. A study reported there were higher serum levels of alkaline phosphatase in obese than in the non obese. With elevated alkaline phosphatase levels there is an increase in disproportionate intracellular fat depots and thereby releasing itself into the bloodstream. The relationship between alkaline phosphatase and obesity is still being tested.
Elevated serum levels of alkaline phosphatase has been associated with Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD). Recently, studies have shown that elevated levels may predict mortality independent of bone metabolism factors and liver function tests in CKD. This distinction is indicated by the markers of inflammations specifically from C-reactive protein (CRP) with elevated levels of alkaline phosphatase. Hence, elevated serum alkaline phosphatase activity may be a marker for inflammation because of its association with elevated levels of CRP.
Elevated alkaline phosphatase in patients with cancer normally spans throughout the bones or liver. Metastasize that exist in the lung, breast, prostate, colon, thyroid, and further organs can penetrate in the liver or bone. Yet, cancers that are already present in certain organs and tissues can produce alkaline phosphatase elevations if metastasis is not present. Isoenzymes, which are certain forms of alkaline phosphatase generated by these tumors, enlarges the total volume of alkaline phosphatase levels on experiential studies. The Regan isoenzyme is one of the best studies of these isoenzymes that is linked to several human cancers. Basically, the Regan isozenzyme is an alkaline phosphatase that is located in the placenta and associated with the gonadal and urologic cancers.
...
Wikipedia
