Egyptian mongoose
| Egyptian mongoose | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | Herpestidae |
| Subfamily: | Herpestinae |
| Genus: | Herpestes |
| Species: | H. ichneumon |
| Binomial name | |
|
Herpestes ichneumon (Linnaeus, 1758) |
|
 |
|
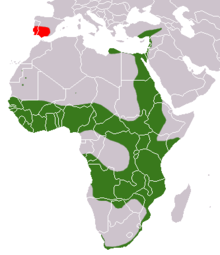
| Egyptian mongoose range (green – native, red – possibly introduced) |
|
The Egyptian mongoose (Herpestes ichneumon), also known as the ichneumon, is a species of mongoose. It may be a reservoir host for visceral leishmaniasis in Sudan.
This mongoose can be found in Egypt, Libya, Spain, Portugal, Israel, Palestine, and most of sub-Saharan Africa, except for central Democratic Republic of the Congo, and arid regions of southern Africa.
In Europe, it occurs mostly in the Iberian Peninsula, where it would have been introduced during the Arab occupation (which lasted, in whole, from 711 AD through 1492 AD, though more markedly in certain southern areas). The Moors may have imported this mongoose, and probably also the genet (Genetta genetta), to hunt rats. Some individuals, escaping captivity, would have become feral. It is known as "meloncillo" in Spanish and "sacarrabos" ("tail robber") in Portuguese.
It prefers to live in forests, savanna, or scrub, but never far from water.
The Egyptian mongoose has a body 48–60 cm long, and a 33–54 cm tail. It weighs 1.7–4 kg.
The Egyptian mongoose has a slender body, with a pointed snout and small ears. It has 35–40 teeth, with highly developed carnassials, used for shearing meat. Its long, coarse fur ranges in colour from grey to reddish brown and is ticked with brown or yellow flecks. Their tails have black tips. The hind feet and a small area around the eyes are furless.
Males and females become sexually mature at two years of age. Mating occurs in July or August, and after a gestation period of 11 weeks, the female gives birth to 2–4 young. Egyptian mongooses are blind and hairless when born, but open their eyes after about a week.
The Egyptian mongoose is diurnal. It is often solitary, but can live in pairs or in groups of 3–7 animals, usually consisting of a male, several females, and their young. Offspring are usually cared for up to 1 year, occasionally longer, though they are capable of foraging for themselves after 4 months, and are forced to compete for food brought back them after that age.
...
Wikipedia

