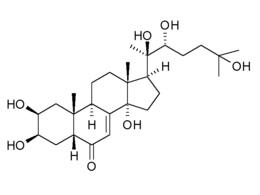
Ecdysterone
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Biological half-life | 4-9 hours |
| Excretion | Urinary:?% |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C27H44O7 |
| Molar mass | 480.63 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20-Hydroxyecdysone (ecdysterone or 20E) is a naturally occurring ecdysteroid hormone which controls the ecdysis (moulting) and metamorphosis of arthropods. It is therefore one of the most common moulting hormones in insects, crabs, etc. It is also a phytoecdysteroid produced by various plants, including Cyanotis vaga, where its purpose is presumably to disrupt the development and reproduction of insect pests. In arthropods, 20-hydroxyecdysone acts through the ecdysone receptor. Although mammals lack this receptor, 20-hydroxyecdysone may affect mammalian (including human) biological systems in vitro, but there is uncertainty whether any in vivo or physiological effects occur. 20-Hydroxyecdysone is an ingredient of some supplements that aim to enhance physical performance, but there is no clinical evidence for this effect.
The primary sources of 20-hydroxyecdysone in larvae are the prothoracic gland, ring gland, gut, and fat bodies. These tissues convert dietary cholesterol into the mature forms of the hormone 20-hydroxyecdysone. For the most part these glandular tissues are lost in the adult with exception of the fat body, which is retained as a sheath of lipid tissue surrounding the brain and organs of the abdomen. In the adult female the ovary is a substantial source of 20-hydroxyecdysone production. Adult males are left with, so far as is currently known, one source of 20-hydroxyecdysone which is the fat body tissue. These hormone producing tissues express the ecdysone receptor throughout development, possibility indicating a functional feedback mechanism.
An ecdysteroid is a type of steroid hormones in insects that are derived from enzymatic modification of cholesterol by p450 enzymes. This occurs by a mechanism similar to steroid synthesis in vertebrates. Ecdysone and 20-hydroxyecdysone regulate larval molts, onset of puparium formation, and metamorphosis. Being that these hormones are hydrophobic, they traverse lipid membranes and permeate the tissues of an organism. Indeed, the main receptor of these hormone signals - the ecdysone receptor - is an intracellular protein.
...
Wikipedia
