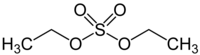
Diethyl sulfate
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Sulfuric acid diethyl ester
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.536 |
| KEGG | |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number | WS7875000 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C4H10O4S | |
| Molar mass | 154.18 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.2 g/mL |
| Melting point | −25 °C (−13 °F; 248 K) |
| Boiling point | 209 °C (408 °F; 482 K) (decomposes) |
| 0.7 g/100 mL | |
| Vapor pressure | 0.29 mm Hg |
| -86.8·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
|
EU classification (DSD) (outdated)
|
Toxic (T) Carc. Cat. 2 Muta. Cat. 2 |
| R-phrases (outdated) | R45 R46 R20/21/22 R34 |
| S-phrases (outdated) | S53 S45 |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | 104 °C (219 °F; 377 K) |
| Related compounds | |
|
Related compounds
|
Dimethyl sulfate; diethyl sulfite |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Diethyl sulfate is a highly toxic and likely carcinogenic chemical compound with formula (C2H5)2SO4. It occurs as a colorless, oily liquid with a faint peppermint odor and is corrosive.
Diethyl sulfate is used as an alkylating agent to prepare ethyl derivatives of phenols, amines, and thiols. It is used to manufacture dyes and textiles.
Diethyl sulfate is a strong alkylating agent which ethylates DNA and thus is genotoxic. There is not sufficient evidence for the carcinogenic properties of diethyl sulfate in humans, but there is in animals. It is classified as a Group 2A carcinogen by the IARC
It can be prepared by absorbing ethylene into concentrated sulfuric acid or by fuming sulfuric acid into diethyl ether or ethanol.
...
Wikipedia

