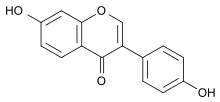
Daidzein
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
7-Hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl) chromen-4-one
|
|
| Other names
4',7-Dihydroxyisoflavone
Daidzeol Isoaurostatin |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
486-66-8 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:28197 |
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL8145 |
| ChemSpider |
4445025 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.942 |
| 2828 | |
| KEGG |
C10208 |
| PubChem | 5281708 |
| UNII |
6287WC5J2L |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C15H10O4 | |
| Molar mass | 254.23 g/mol |
| Appearance | Pale yellow prisms |
| Melting point | 315 to 323 °C (599 to 613 °F; 588 to 596 K) (decomposes) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Daidzein structurally belongs to the group of isoflavones.
Daidzein and other isoflavone compounds, such as genistein, are present in a number of plants and herbs like Kwao Krua (Pueraria mirifica) and Kudzu (Pueraria lobata). It can also be found in Maackia amurensis cell cultures.
Daidzein can be found in food such as soybeans and soy products like tofu and textured vegetable protein. Soy isoflavones are a group of compounds found in and isolated from the soybean. Of note, total isoflavones in soybeans are—in general—37 percent daidzein, 57 percent genistein and 6 percent glycitein, according to USDA data. Soy germ contains 41.7 percent daidzein.
Daidzein can be converted to its end metabolite S-equol in some humans based on the presence of certain intestinal bacteria. Based on several decades of research, S-equol has potential for significant health benefits.
Daidzein has no classification in the United States, where it is not considered to be generally recognized as safe (GRAS), and has not been approved as a drug for any indication. It is a component of foods and dietary supplements derived from soy. Dietary supplements are not regulated as drugs in the U.S., and the labeling of dietary supplements in the U.S. may not describe the supplement as having any drug activity or effectiveness.
Scientists have studied some of the activities of daidzein in their laboratories, working with cells or with animals such as mice. Studies in cells and in animals sometimes give hints as to what a chemical might do when given to humans, but no one can know what a chemical does in humans until the chemical is tested in a clinical trial.
...
Wikipedia
