Cystic artery
| Cystic artery | |
|---|---|

The cystic artery branches from the hepatic artery proper.
|
|
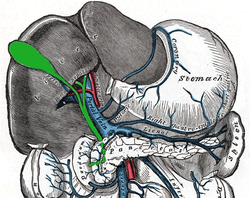
Relationship to other vessels. (Note that relationships are highly variable -- see below.)
|
|
| Details | |
| Source | Right hepatic artery |
| Branches | Superior branch Deep branch |
| Vein | Cystic vein |
| Supplies | Gall bladder and cystic duct |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria cystica |
| Dorlands /Elsevier |
a_61/12154087 |
| TA | A12.2.12.031 |
| FMA | 14835 |
|
Anatomical terminology []
|
|
The cystic artery supplies oxygenated blood to the gallbladder and cystic duct.
In the classic arrangement, occurring with a frequency of approximately 70%, a singular cystic artery originates from the geniculate flexure of the right hepatic artery in the upper portion of the hepatobiliary triangle. A site of origin from a more proximal or distal portion of the right hepatic artery is also considered relatively normal.
After separating from the right hepatic artery, the cystic artery travels superiorly to the cystic duct and produces 2 to 4 minor branches, known as Calot’s arteries, that supply part of the cystic duct and cervix of the gallbladder before dividing into the major superficial and deep branches at the superior aspect of the gallbladder neck:
When superficial and deep branches of the cystic artery do not share a common origin it is defined as a double cystic artery occurring with a frequency of 15%.
The deep branch consistently arises from the right hepatic artery which is generally also the source of origin of the superficial branch, however in some cases it has been found to initiate from the anterior segmental artery, middle hepatic artery, left hepatic artery, superior mesenteric artery, gastroduodenal artery or retroduodenal artery.
Approximately half of superficial cystic arteries have been shown to enter through the hepatobiliary triangle, while deep cystic arteries are often quite small in length and diameter. Tripling of the cystic artery is very rare, occurring in between 0-0.3% of cases.
Unusual anatomy of the right hepatic can itself affect the path and form of the cystic artery, with the most frequent variation resulting from an aberrant origin of the right hepatic artery which is described in between 2-16% of cases.
Generally this anomalous source is the superior mesenteric artery or more rarely the abdominal aorta, producing what has been described as a "replacing right hepatic artery", passing through the hepatobiliary triangle and running posterior and parallel to the cystic duct.
Because of the close proximity to the gallbladder to the (replacing) right hepatic artery a "caterpillar" or "Moynihan's" hump may form and this artery generally produces multiple short cystic branches rather than a single cystic artery.
...
Wikipedia
