Cystathionine gamma-lyase
| cystathionine gamma-lyase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
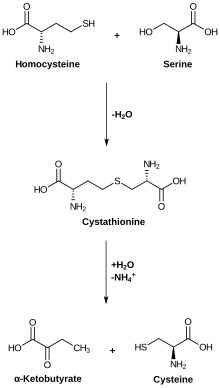
Cysteine metabolism. Cystathionase catalyzes the lower reaction.
|
|||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 4.4.1.1 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 9012-96-8 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / EGO | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Search | |
|---|---|
| PMC | articles |
| PubMed | articles |
| NCBI | proteins |
| cystathionase (cystathionine gamma-lyase) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | CTH |
| Entrez | 1491 |
| HUGO | 2501 |
| OMIM | 607657 |
| RefSeq | NM_001902 |
| UniProt | P32929 |
| Other data | |
| EC number | 4.4.1.1 |
| Locus | Chr. 1 p31.1 |
Cystathionine gamma-lyase (CTH or CSE; also cystathionase) is an enzyme which breaks down cystathionine into cysteine, α-ketobutyrate, and ammonia. Pyridoxal phosphate is a prosthetic group of this enzyme.
Cystathionine gamma-lyase also catalyses the following elimination reactions:
In some bacteria and mammals, including humans, this enzyme takes part in generating hydrogen sulfide. Hydrogen sulfide is one of a few gases that was recently discovered to have a role in cell signaling in the body.
Cystathionase uses pyridoxal phosphate to facilitate the cleavage of the sulfur-gamma carbon bond of cystathionine, resulting in the release of cysteine. Afterwards the external ketimine is hydrolyzed, causing the release of α-ketobutyrate. The lysine residue reforms the internal aldimine by kicking off the ammonia leaving group.
The amino group on cystathionine is deprotonated and undergoes a nucleophilic attack of the internal aldimine. An additional deprotonation by a general base results in the formation of the external aldimine and removal of the lysine residue. The basic lysine residue is then able to deprotonate the alpha carbon, pushing electron density into the nitrogen of the pyridine ring. Pyridoxal phosphate is necessary to stabilize this carbanionic intermediate; otherwise the proton's pKa would be too high. The beta carbon is then deprotonated, creating an alpha-beta unsaturation and pushing a lone pair onto the aldimine nitrogen. To reform the aldimine, this lone pair pushes back down, cleaving the sulfur-gamma carbon bond, resulting in the release of cysteine.
...
Wikipedia
