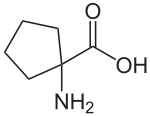
Cycloleucine
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
1-Amino-1-cyclopentanecarboxylic acid
|
|
| Other names
1-Aminocyclopentanecarboxylic acid
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.132 |
| KEGG | |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C6H11NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 129.16 g/mol |
| Appearance | white of beige crystalline flakes or powder |
| Density | 1.207 g/mL |
| Melting point | 320 °C (608 °F; 593 K) |
| Boiling point | 256.1 °C (493.0 °F; 529.2 K) |
| 50 mg/mL | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Irritant |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Cycloleucine is a non-proteinogenic amino acid. It could be classified as a cyclic derivate of norleucine, having two hydrogen atoms less. Leading structure is a cyclopentane-ring. The α-carbon atom is not a stereocenter.
Cycloleucine is a non-metabolisable amino acid and is a specific and reversible inhibitor of nucleic acid methylation, and as such is widely used in biochemical experiments.
...
Wikipedia
