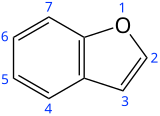
Coumarone
 |
|||
|
|
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Preferred IUPAC name
1-Benzofuran
|
|||
| Other names
Benzofuran
Coumarone Benzo[b]furan |
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.439 | ||
| KEGG | |||
|
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
|
|||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| C8H6O | |||
| Molar mass | 118.14 g·mol−1 | ||
| Melting point | −18 °C (0 °F; 255 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 173 °C (343 °F; 446 K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
500 mg/kg (mice). | ||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
Benzofuran is the heterocyclic compound consisting of fused benzene and furan rings. This colourless liquid is a component of coal tar. Benzofuran is the "parent" of many related compounds with more complex structures. For example, psoralen is a benzofuran derivative that occurs in several plants.
Benzofuran is extracted from coal tar. It is also obtained by dehydrogenation of 2-ethylphenol.
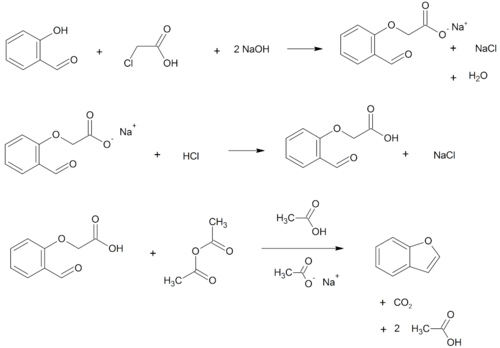
Benzofurans can be prepared by various methods in the laboratory. Notable examples include:
...
Wikipedia