Contrabass clarinet

Ernst Ulrich Deuker, a German jazz musician, with a Selmer contrabass clarinet
|
|
| Woodwind instrument | |
|---|---|
| Classification | Single-reed |
| Developed | 1808 |
| Playing range | |
| Related instruments | |
| Musicians | |
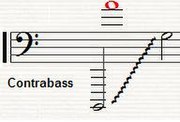
The contrabass clarinet and contra-alto clarinet are the two largest members of the clarinet family that are in common usage. Modern contrabass clarinets are pitched in BB♭, sounding two octaves lower than the common B♭ soprano clarinet and one octave lower than the B♭ bass clarinet. Some contrabass clarinet models have a range extending down to low (written) E♭, while others can play down to low D or further to low C. Some early instruments were pitched in C; Arnold Schoenberg's Fünf Orchesterstücke specifies a contrabass clarinet in A, but there is no evidence of such an instrument ever having existed.
The contrabass clarinet is also sometimes known by the name pedal clarinet, this term referring not to any aspect of the instrument's mechanism but to an analogy between its very low tones and the pedal division of the organ.
Subcontrabass clarinets, lower in pitch than the contrabass, have been built on only an experimental basis.
The EE♭ contra-alto clarinet is sometimes referred to as the "EE♭ contrabass clarinet".
The earliest known contrabass clarinet was the contre-basse guerrière invented in 1808 by a goldsmith named Dumas of Sommières; little else is known of this instrument. The batyphone (also spelled bathyphone, Ger. and Fr. batyphon) was a contrabass clarinet which was the outcome of W. F. Wieprecht's endeavor to obtain a contrabass for the reed instruments. The batyphone was made to a scale twice the size of the clarinet in C, the divisions of the chromatic scale being arranged according to acoustic principles. For convenience in stopping holes too far apart to be covered by the fingers, crank or swivel keys were used. The instrument was constructed of maple-wood, had a clarinet mouthpiece of suitable size connected by means of a cylindrical brass crook with the upper part of the tube and a brass bell. The pitch was two octaves below the clarinet in C, the compass being the same, and thus corresponding to the modern bass tuba. The tone was pleasant and full, but not powerful enough for the contrabass register in a military band. The batyphone had besides one serious disadvantage: it could be played with facility only in its nearly related keys, G and F major. The batyphone was invented and patented in 1839 by F.W. Wieprecht, director general of all the Prussian military bands, and E. Skorra, the court instrument manufacturer of Berlin. In practice the instrument was found to be of little use, and was superseded by the bass tuba.
...
Wikipedia