Congenital diaphragmatic hernia
| Congenital diaphragmatic hernia | |
|---|---|
 |
|
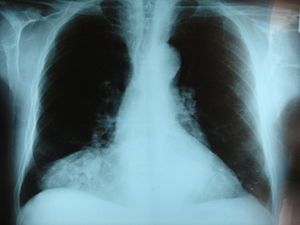
| Morgagni hernia seen on a chest radiograph. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | medical genetics |
| ICD-10 | Q79.0 |
| ICD-9-CM | 756.6 |
| OMIM | 142340 222400 |
| DiseasesDB | 32489 |
| MedlinePlus | 001135 |
| eMedicine | ped/2603 |
| Patient UK | Congenital diaphragmatic hernia |
| MeSH | D006548 |
| GeneReviews | |
| Orphanet | 2140 |
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH) is a birth defect of the diaphragm. The most common type of CDH is a Bochdalek hernia; other types include Morgagni hernia, diaphragm eventration and central tendon defects of the diaphragm. Malformation of the diaphragm allows the abdominal organs to push into the chest cavity, hindering proper lung formation.
CDH is a life-threatening pathology in infants and a major cause of death due to two complications: pulmonary hypoplasia and pulmonary hypertension. Experts disagree on the relative importance of these two conditions, with some focusing on hypoplasia, others on hypertension. Newborns with CDH often have severe respiratory distress which can be life-threatening unless treated appropriately.
The Bochdalek hernia, also known as a postero-lateral diaphragmatic hernia, is the most common manifestation of CDH, accounting for more than 95% of cases. In this instance the diaphragm abnormality is characterized by a hole in the postero-lateral corner of the diaphragm which allows passage of the abdominal viscera into the chest cavity. The majority of Bochdalek hernias (80–85%) occur on the left side of the diaphragm, a large proportion of the remaining cases occur on the right side. To date, it carries a high mortality and an active area of clinical research.
This rare anterior defect of the diaphragm is variably referred to as Morgagni, retrosternal, or parasternal hernia. Accounting for approximately 2% of all CDH cases, it is characterized by herniation through the foramina of Morgagni which are located immediately adjacent and posterior to the xiphoid process of the sternum.
The diagnosis of congenital diaphragmatic eventration is used when there is abnormal displacement (i.e. elevation) of part or all of an otherwise intact diaphragm into the chest cavity. This rare type of CDH occurs because in the region of eventration the diaphragm is thinner, allowing the abdominal viscera to protrude upwards.
...
Wikipedia
