Colles' fracture
| Colles' fracture | |
|---|---|
| Classification and external resources | |
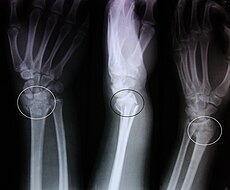
An X-ray image of a fractured radius showing the characteristic Colles' fracture with displacement and angulation of the distal end of the radius
|
|
| ICD-10 | S52.5 |
| AO | 23-A2.2 |
| MeSH | 68003100 |
A Colles' fracture is a fracture of the distal radius in the forearm with dorsal (posterior) and radial displacement of the wrist and hand. The fracture is sometimes referred to as a "dinner fork" or "bayonet" deformity due to the shape of the resultant forearm. Colles' fractures are often seen in people with osteoporosis.
The term of Colles fracture is classically used to describe a fracture at the distal end of the radius, at its cortico-cancellous junction. However, now the term tends to be used loosely to describe any fracture of the distal radius, with or without involvement of the ulna, that has dorsal displacement of the fracture fragments. Colles himself described it as a fracture that “takes place at about an inch and a half (38mm) above the carpal extremity of the radius” and “the carpus and the base of metacarpus appears to be thrown backward”.
The classic Colles fracture has the following characteristics:
The fracture is most commonly caused by people falling onto a hard surface and breaking their fall with outstretched arms - falling with wrists flexed would lead to a Smith's fracture. It can also be caused by overuse. Originally it was described in elderly and/or post-menopausal women. It usually occurs about three to five centimetres proximal to the radio-carpal joint with posterior and lateral displacement of the distal fragment resulting in the characteristic "dinner fork" or "bayonet" like deformity. Colles' fracture is a common fracture in people with osteoporosis, second only to vertebral fractures.
Management depends on the severity of the fracture. An undisplaced fracture may be treated with a cast alone. The cast is applied with the distal fragment in palmar flexion and ulnar deviation. A fracture with mild angulation and displacement may require closed reduction. There is some evidence that immobilization with the wrist in dorsiflexion as opposed to palmarflexion results in less redisplacement and better functional status. Significant angulation and deformity may require an open reduction and internal fixation or external fixation. The volar forearm splint is best for temporary immobilization of forearm, wrist and hand fractures, including Colles' fracture. There are several established instability criteria: dorsal tilt >20°, comminuted fracture, abruption of the ulnar styloid process, intraarticular displacement >1mm, loss of radial height >2mm.
...
Wikipedia
