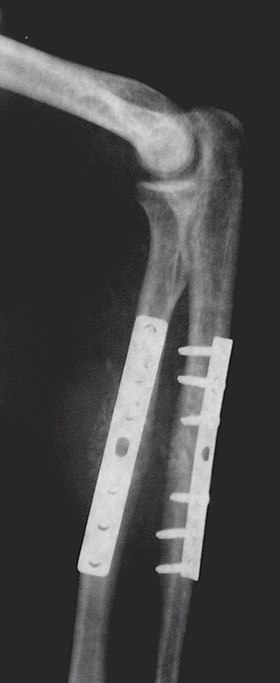
Open reduction internal fixation
| Internal fixation | |
|---|---|
| Intervention | |
|
|
| ICD-9-CM | 78.5 |
| MeSH | D005593 |
Internal fixation is an operation in orthopedics that involves the surgical implementation of implants for the purpose of repairing a bone, a concept that dates to the mid-nineteenth century and was made applicable for routine treatment in the mid-twentieth century. An internal fixator may be made of stainless steel or titanium.
Types of internal fixators include:
Open Reduction Internal Fixation (ORIF) involves the implementation of implants to guide the healing process of a bone, as well as the open reduction, or setting, of the bone. Open reduction refers to open surgery to set bones, as is necessary for some fractures. Internal fixation refers to fixation of screws and/or plates, intramedullary bone nails (femur, tibia, humerus) to enable or facilitate healing. Rigid fixation prevents micro-motion across lines of fracture to enable healing and prevent infection, which happens when implants such as plates (e.g. dynamic compression plate) are used. Open Reduction Internal Fixation techniques often are used in cases involving serious fractures such as comminuted or displaced fractures or, in cases where the bone otherwise would not heal correctly with casting or splinting alone.
Risks and complications may include bacterial colonization of the bone, infection, stiffness and loss of range of motion, non-union, mal-union, damage to the muscles, nerve damage and palsy, arthritis, tendonitis, chronic pain associated with plates, screws, and pins, compartment syndrome, deformity, audible popping and snapping, and possible future surgeries to remove the hardware.
...
Wikipedia
