Cochineal beetle
| Cochineal | |
|---|---|
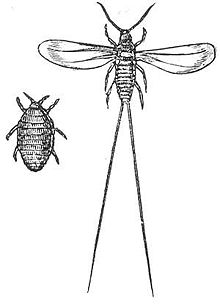 |
|
| Female (left) and male (right) cochineals | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Hemiptera |
| Family: | Dactylopiidae |
| Genus: | Dactylopius |
| Species: | D. coccus |
| Binomial name | |
|
Dactylopius coccus Costa, 1835 |
|
| Synonyms | |
|
Coccus cacti Linnaeus, 1758 |
|
Coccus cacti Linnaeus, 1758
Pseudococcus cacti Burmeister, 1839
The cochineal (/kɒtʃɪˈniːl/ koch-i-NEEL or /ˈkɒtʃɪniːl/ KOCH-i-neel; Dactylopius coccus) is a scale insect in the suborder Sternorrhyncha, from which the natural dye carmine is derived. A primarily sessile parasite native to tropical and subtropical South America as well as Mexico and Arizona, this insect lives on cacti in the genus Opuntia, feeding on plant moisture and nutrients. These insects are found on the pads of prickly pear cacti, then are brushed off and dried.
The insect produces carminic acid that deters predation by other insects. Carminic acid, typically 17-24% of dried insects' weight, can be extracted from the body and eggs, then mixed with aluminium or calcium salts to make carmine dye, also known as cochineal. Today, carmine is primarily used as a colorant in food and in lipstick.
...
Wikipedia
