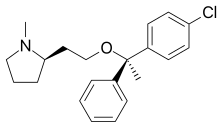
Clemastine
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682542 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 39.2% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Biological half-life | 21.3 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H26ClNO |
| Molar mass | 343.9 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
Clemastine, also known as meclastin, is an antihistamine and anticholinergic. Unlike loratadine or fexofenadine, clemastine is a sedating antihistamine; however, it exhibits fewer other side effects than most of the widely used antihistamines. Clemastine is also classified as an antipruritic (i.e., it stops itching).
Clemastine is indicated for use in treating allergic rhinitis, such as sneezing, rhinorrhea, pruritus and lacrimation.
Overdosage symptoms are paradoxical, ranging from CNS depression to stimulation. Stimulation is most common in children, and is usually followed by excitement, hallucinations, ataxia, loss of coordination, muscle twitching, athetosis, hyperthermia, cyanosis, convulsions, tremors, and hyperreflexia. This may be followed by postictal depression and cardiovascular/respiratory arrest. Other common overdose symptoms include dry mouth, fixed dilated pupils, flushing of the face, and pyrexia. In adults, overdose usually leads to CNS depression, ranging from drowsiness to coma.
Clemastine is an antihistamine with anticholinergic and sedative effects. Antihistamines competitively bind to histamine receptor sites, thus reducing the neurotransmitter's effects. Effects of histamine (which are countered by antihistamines) include:
...
Wikipedia
