Cholera morbus
| Gastroenteritis | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Gastro, stomach bug, stomach virus, stomach flu, gastric flu, gastrointestinitis |
 |
|
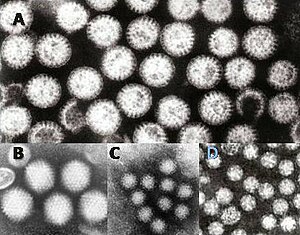
| Gastroenteritis viruses: A = rotavirus, B = adenovirus, C = norovirus and D = astrovirus. The virus particles are shown at the same magnification to allow size comparison. | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
| Symptoms | Diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fever |
| Complications | Dehydration |
| Causes | Viruses, bacteria, parasites, fungus |
| Diagnostic method | Based on symptom, occasionally stool culture |
| Prevention | Hand washing, drinking clean water, proper disposal of human waste, breastfeeding |
| Treatment | Oral rehydration solution (combination of water, salts, and sugar), intravenous fluids |
| Frequency | 2.4 billion (2015) |
| Deaths | 1.3 million (2015) |
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
Gastroenteritis, also known as infectious diarrhea, is inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract that involves the stomach and small intestine. Signs and symptoms include some combination of diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.Fever, lack of energy, and dehydration may also occur. This typically lasts less than two weeks. It is unrelated to influenza though it has been called the "stomach flu".
Gastroenteritis can be due to infections by viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungus. The most common cause is viruses. In children rotavirus is the most common cause of severe disease. In adults, norovirus and Campylobacter are common. Transmission may occur due to eating improperly prepared foods, drinking contaminated water, or through close contact with an individual who is infected. Testing to confirm the diagnosis is typically not needed.
Prevention includes hand washing with soap, drinking clean water, proper disposal of human waste, and breastfeeding babies instead of using formula. The rotavirus vaccine is recommended in children. Treatment involves getting enough fluids. For mild or moderate cases, this can typically be achieved by drinking oral rehydration solution (a combination of water, salts, and sugar). In those who are breast fed, continued breastfeeding is recommended. For more severe cases, intravenous fluids may be needed. Fluids may also be given by a nasogastric tube.Zinc supplementation is recommended in children.Antibiotics are generally not needed.
...
Wikipedia
