Stool culture
| Stool test | |
|---|---|
| Medical diagnostics | |
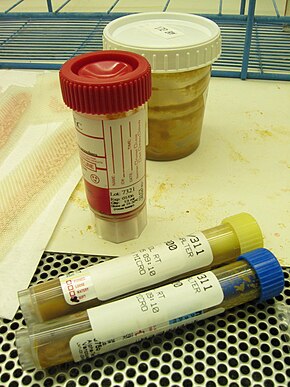
Transport vials filled with human feces for stool testing. Yellow and blue tops for parasite testing, red top for stool cultures and the white top was provided by the patient with the sample.
|
A stool test involves the collection and analysis of fecal matter to diagnose the presence or absence of a medical condition.
The patient and/or health care worker in the office or at the bedside is able to make some important observations.
One of the most common stool tests, the fecal occult blood test can be used to diagnose many conditions that cause bleeding in the gastrointestinal system including colorectal cancer or stomach cancer. Cancers, and to a lesser extent, precancerous lesions, shed abnormal cells into the stool.> Cancers and precancerous lesions (polyps) that are ulcerated or rubbed by passing stool also may shed blood into the stool, which can be identified by a hemoglobin assay.
The American Cancer Society recommends screening with either DNA testing every 3 years, guaiac fecal occult blood test, or fecal immunochemical test every year starting at age 50. Other options include sigmoidoscopy or virtual colonoscopy (CT colonography) every five years or colonoscopy every 10 years.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force published an updated colorectal cancer screening recommendation statement in 2016.
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) published screening guidelines in 2016.
In 2016 the National Committee for Quality Assurance (NCQA) issued an update to the Healthcare Effectiveness Data and Information Set (HEDIS) for 2017.
A DNA test using stool samples was approved in August 2014 by the FDA as a screening test for non-symptomatic, average-risk adults 50 years or older. A 2017 study found this testing to be less cost effective as compared to colonoscopy or fecal occult blood testing. Three-year sDNA screening has been estimated to cost $11,313 per quality adjusted life year (QALY) compared with no screening.
...
Wikipedia
