Chlamydia trachomatis infection
| Chlamydia infection | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Chlamydia |
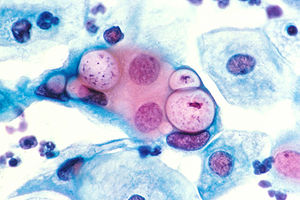 |
|
| Pap smear showing C. trachomatis (H&E stain) | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease, gynecology, urology |
| Symptoms | None, vaginal discharge, discharge from the penis, burning with urination |
| Complications | Pain in the testicles, pelvic inflammatory disease, infertility, ectopic pregnancy |
| Usual onset | Few weeks following exposure |
| Causes | Chlamydia trachomatis spread by sex or childbirth |
| Diagnostic method | Urine or swab of the cervix, vagina, or urethra |
| Prevention | Not having sex, condoms, sex with only one non–infected person |
| Treatment | Antibiotics (azithromycin or doxycycline) |
| Frequency | 4.2% (women), 2.7% (men) |
| Deaths | ~200 (2015) |
| Classification |
· ·
|
|---|---|
| External resources |
Chlamydia infection, often simply known as chlamydia, is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis. Most people who are infected have no symptoms. When symptoms do develop this can take a few weeks following infection to occur. Symptoms in women may include vaginal discharge or burning with urination. Symptoms in men may include discharge from the penis, burning with urination, or pain and swelling of one or both testicles. The infection can spread to the upper genital tract in women causing pelvic inflammatory disease which may result in future infertility or ectopic pregnancy. Repeated infections of the eyes that go without treatment can result in trachoma, a common cause of blindness in the developing world.
Chlamydia can be spread during vaginal, anal, or oral sex, and can be passed from an infected mother to her baby during childbirth. The eye infections may also be spread by personal contact, flies, and contaminated towels in areas with poor sanitation.Chlamydia trachomatis only occurs in humans. Diagnosis is often by screening which is recommended yearly in sexually active women under the age of twenty five, others at higher risk, and at the first prenatal visit. Testing can be done on the urine or a swab of the cervix, vagina, or urethra. Rectal or mouth swabs are required to diagnose infections in those areas.
...
Wikipedia
