Cauda equina
| Cauda equina | |
|---|---|
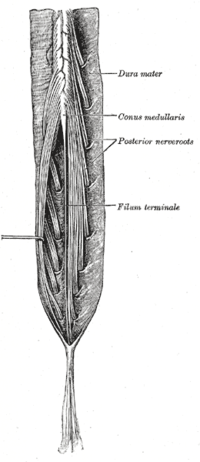
Cauda equina and filum terminale seen from behind.
|
|

Human caudal spinal cord anterior view
|
|
| Details | |
| Artery | Iliolumbar artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Cauda equina |
| MeSH | A08.800.800.720.725.150 |
| TA | A14.2.00.036 |
| FMA | 52590 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
The cauda equina (Latin for "horse's tail") is a bundle of spinal nerves and spinal nerve roots, consisting of the second through fifth lumbar nerve pairs, the first through fifth sacral nerve pairs, and the coccygeal nerve, all of which arise from the lumbar enlargement and the conus medullaris of the spinal cord. The cauda equina occupies the lumbar cistern, a subarachnoid space inferior to the conus medullaris. The nerves that compose the cauda equina innervate the pelvic organs and lower limbs to include motor innervation of the hips, knees, ankles, feet, internal anal sphincter and external anal sphincter. In addition, the cauda equina extends to sensory innervation of the perineum and, partially, parasympathetic innervation of the bladder.
In humans, the spinal cord stops growing in infancy and the end of the spinal cord is about the level of the third lumbar vertebra, or L3, at birth. Because the bones of the vertebral column continue to grow, by about 12 months of age, the end of the cord reaches its permanent position at the level of L1 or L2 (closer to the head). However, due to normal anatomical variations, the final cord end position may occur anywhere from T12 twelfth thoracic vertebra (T12) to L3. Individual spinal nerve roots arise from the cord as they do closer to the head, but as the differential growth occurs, the top end of the nerve stays attached to the spinal cord while the lower end of the nerve exits the spinal column at its proper level. This results in a "bundle"-like structure of nerve fibers that extends caudally from the end of the spinal cord, gradually declining in number further down as individual pairs leave the spinal column.
...
Wikipedia
