Carphedon
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Phenotropil; Carphedon |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral (tablets) |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ~100% |
| Metabolism | None |
| Biological half-life | 3–5 hours |
| Excretion | Urine (~40%), bile and perspiration (~60%) |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.214.874 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
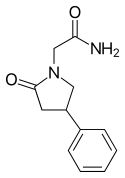
| Formula | C12H14N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 218.3 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
| Boiling point | 486.4 °C (907.5 °F) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Phenylpiracetam (INN: fonturacetam, brand names Phenotropil, Carphedon), also called is a phenylated analog of the drug piracetam which was developed in 1983 in Russia where it is available as a prescription drug. Research on animals has indicated that phenylpiracetam may have anti-amnesic, antidepressant, anticonvulsant, antipsychotic, anxiolytic, and memory enhancement effects.
A few small clinical studies have shown possible links between prescription of phenylpiracetam and improvement in a number of encephalopathic conditions, including lesions of cerebral blood pathways, traumatic brain injury and certain types of glioma.
Phenylpiracetam reverses the depressant effects of the benzodiazepine diazepam, increases operant behavior, inhibits post-rotational nystagmus, prevents retrograde amnesia, and has anticonvulsant properties.
Phenylpiracetam is typically prescribed as a general stimulant or to increase tolerance to extreme temperatures and stress.
...
Wikipedia
