Carotid vessels
| Common carotid artery | |
|---|---|
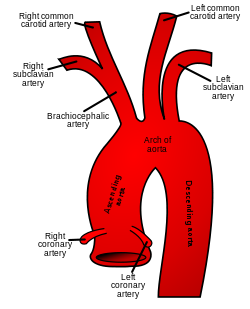
The common carotid artery arises directly from the aorta on the left, and as a branch of the brachiocephalic trunk on the right
|
|
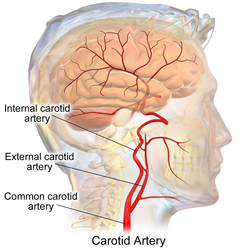
The common carotid artery and its main branches
|
|
| Details | |
| Precursor | aortic arch 3 |
| Source | aortic arch, brachiocephalic artery |
| Branches | internal carotid artery, external carotid artery |
| Vein | internal jugular vein |
| Supplies | head and neck |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Arteria carotis communis |
| MeSH | A07.231.114.186.200 |
| Dorlands /Elsevier |
a_61/12153659 |
| TA | A12.2.04.006 |
| FMA | 3939 |
|
Anatomical terminology []
|
|
In anatomy, the left and right common carotid arteries (English: /kəˈrɒtɪd/) are arteries that supply the head and neck with oxygenated blood; they divide in the neck to form the external and internal carotid arteries.
The common carotid arteries are present on the left and right sides of the body. These arteries originate from different arteries, but follow symmetrical courses. The right common carotid originates in the neck from the brachiocephalic trunk; the left from the aortic arch in the thorax. These split into the external and internal carotid arteries at the upper border of the thyroid cartilage, at around the level of the fourth cervical vertebra.
The left common carotid artery can be thought of as having two parts: a thoracic (chest) part and a cervical (neck) part. The right common carotid originates in or close to the neck, so contains only a small thoracic portion. There are studies in the bioengineering literature that have looked into characterizing the geometric structure of the common carotid artery from both qualitative and mathematical (quantitative) standpoints.
The average diameters of the common carotids in adult males and females are 6.5 mm and 6.1 mm respectively.
Only the left common carotid artery has a substantial presence in the thorax. It originates directly from the aortic arch, and travels upward through the superior mediastinum to the level of the left sternoclavicular joint.
During the thoracic part of its course, the left common carotid artery is related to the following structures: In front, it is separated from the manubrium of the sternum by the sternohyoid and sternothyroid muscles, the anterior portions of the left pleura and lung, the left brachiocephalic vein, and the remains of the thymus; behind, it lies on the trachea, esophagus, left recurrent laryngeal nerve, and thoracic duct.
...
Wikipedia
