Cardio-thoracic surgery
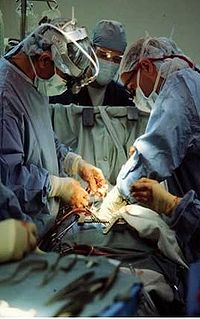
Cardiothoracic surgeon performs an operation.
|
|
| Occupation | |
|---|---|
| Names |
|
| Specialty | |
|
Activity sectors
|
Medicine, Surgery |
| Description | |
|
Education required
|
|
|
Fields of
employment |
Hospitals, Clinics |
| Cardiac surgery | |
|---|---|
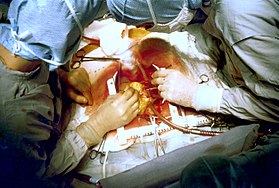
Two cardiac surgeons performing a cardiac surgery known as coronary artery bypass surgery. Note the use of a steel retractor to forcefully maintain the exposure of the patient's heart.
|
|
| ICD-9-CM | 35-37 |
| MeSH | D006348 |
| OPS-301 code | 5-35...5-37 |
Cardiothoracic surgery (also known as thoracic surgery) is the field of medicine involved in surgical treatment of organs inside the thorax (the chest)—generally treatment of conditions of the heart (heart disease) and lungs (lung disease). In most countries, cardiac surgery (involving the heart and the great vessels) and general thoracic surgery (involving the lungs, esophagus, thymus, etc.) are separate surgical specialties; the exceptions are the United States, Australia, New Zealand, and some EU countries, such as the United Kingdom and Portugal.
A cardiac surgery residency typically comprises anywhere from 4 to 16 years (or longer) of training to become a fully qualified surgeon. Cardiac surgery training may be combined with thoracic surgery and / or vascular surgery and called cardiovascular (CV) / cardiothoracic (CT) / cardiovascular thoracic (CVT) surgery. Cardiac surgeons may enter a cardiac surgery residency directly from medical school, or first complete a general surgery residency followed by a fellowship. Cardiac surgeons may further sub-specialize cardiac surgery by doing a fellowship in a variety of topics including: pediatric cardiac surgery, cardiac transplantation, adult acquired heart disease, weak heart issues, and many more problems in the heart.
The highly competitive Surgical Education and Training (SET) program in Cardiothoracic Surgery is six years in duration, usually commencing several years after completing medical school. Training is administered and supervised via a bi-national (Australia and New Zealand) training program. Multiple examinations take place throughout the course of training, culminating in a final fellowship exam in the final year of training. Upon completion of training, surgeons are awarded a Fellowship of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons (FRACS), denoting that they are qualified specialists. Trainees having completed a training program in General Surgery and have obtained their FRACS will have the option to complete fellowship training in Cardiothoracic Surgery of four year in duration, subject to college approval. It takes around eight to ten years minimum of post-graduate (post-medical school) training to qualify as a cardiothoracic surgeon. Competition for training places and for public (teaching) hospital places is very high currently, leading to concerns regarding workforce planning in Australia.
...
Wikipedia
