Candida (fungus)
| Candida | |
|---|---|
 |
|
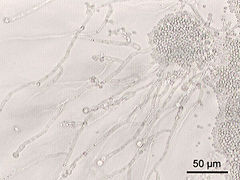
| Candida albicans at 200X magnification | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Ascomycota |
| Class: | Saccharomycetes |
| Order: | Saccharomycetales |
| Family: | Saccharomycetaceae |
| Genus: |
Candida Berkh. (1923) |
| Type species | |
|
Candida vulgaris Berkh. (1923) |
|
Candida is a genus of yeasts and is the most common cause of fungal infections worldwide. Many species are harmless commensals or endosymbionts of hosts including humans; however, when mucosal barriers are disrupted or the immune system is compromised they can invade and cause disease.Candida albicans is the most commonly isolated species, and can cause infections (candidiasis or thrush) in humans and other animals. In winemaking, some species of Candida can potentially spoil wines.
Many species are found in gut flora, including C. albicans in mammalian hosts, whereas others live as endosymbionts in insect hosts.Systemic infections of the bloodstream and major organs (candidemia or invasive candidiasis), particularly in immunocompromised patients, affect over 90,000 people a year in the U.S.
The genome of several Candida species has been sequenced.
Antibiotics promote yeast infections, including gastrointestinal Candida overgrowth, and penetration of the GI mucosa. While women are more susceptible to genital yeast infections, men can also be infected. Certain factors, such as prolonged antibiotic use, increase the risk for both men and women. People with diabetes or impaired immune systems, such as those with HIV, are more susceptible to yeast infections.
Candida antarctica is a source of industrially important lipases.
When grown in a laboratory, Candida appears as large, round, white or cream (albicans means "whitish" in Latin) colonies, which emit a yeasty odor on agar plates at room temperature.C. albicans ferments glucose and maltose to acid and gas, sucrose to acid, and does not ferment lactose, which help to distinguish it from other Candida species.
...
Wikipedia
