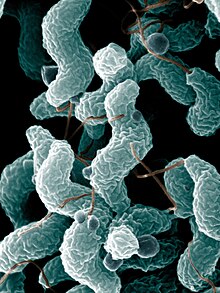
Campylobacter jejuni
| Campylobacter jejuni | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Campylobacter jejuni | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Bacteria |
| Phylum: | Proteobacteria |
| Class: | Epsilonproteobacteria |
| Order: | Campylobacterales |
| Family: | Campylobacteraceae |
| Genus: | Campylobacter |
| Species: | C. jejuni |
| Binomial name | |
|
Campylobacter jejuni (Jones et al., 1931) Veron & Chatelain, 1973 |
|
Campylobacter jejuni (CAM-puh-low-back-ter juh-JUNE-eye) is one of the most common causes of food poisoning in the United States. The vast majority of cases occur as isolated events, not as part of recognized outbreaks. Active surveillance through the Foodborne Diseases Active Surveillance Network (FoodNet) indicates that about 14 cases are diagnosed each year for each 100,000 persons in the population.Campylobacter jejuni is in a genus of bacteria that is among the most common causes of bacterial infections in humans worldwide. The name means "curved rod", deriving from the Greek campylos (curved) and baktron (rod). It has been noted that there "is wide diversity in the genus. The species are metabolically and genetically different to the extent that one can question whether one genus is adequate to house all of the species." Of its many species, C. jejuni is considered one of the most important from both a microbiological and public health perspective.
C. jejuni is also commonly found in animal feces. Campylobacter is a helical-shaped, nonspore-forming, Gram-negative, microaerophilic, nonfermenting bacterium forming motile rods with a single polar flagellum, which are also oxidase-positive and grow optimally at 37 to 42 °C. This species of pathogenic bacteria is one of the most common causes of human gastroenteritis in the world. Food poisoning caused by Campylobacter species can be severely debilitating, but is rarely life-threatening. It has been linked with subsequent development of Guillain–Barré syndrome, which usually develops two to three weeks after the initial illness.
Campylobacteriosis is an infectious disease caused by bacteria of the genus Campylobacter. In most people who become ill with campylobacteriosis, symptoms develop within two to five days of exposure to the organism and illness typically lasts seven days following onset. Infection with C. jejuni usually results in enteritis, which is characterised by abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever, and malaise. Diarrhea itself can vary in severity from loose to bloody stools. The disease is usually self-limiting. However, it does respond to antibiotics. Severe (accompanying fevers, blood in stools) or prolonged cases may require erythromycin, azithromycin, ciprofloxacin, or norfloxacin. Fluid replacement may be required for serious cases.
...
Wikipedia
