Calabar bean
| Calabar bean | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| (unranked): | Angiosperms |
| (unranked): | Eudicots |
| (unranked): | Rosids |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Subfamily: | Faboideae |
| Genus: | Physostigma |
| Species: | P. venenosum |
| Binomial name | |
|
Physostigma venenosum Balf. |
|
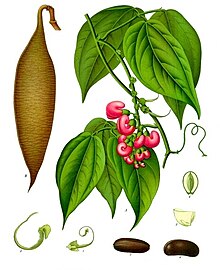
Physostigma venenosum (the Calabar bean or ordeal bean) is the seed of a leguminous plant, a native of tropical Africa, poisonous to humans. It derives the first part of its scientific name from a curious beak-like appendage at the end of the stigma, in the centre of the flower; this appendage, though solid, was supposed to be hollow (hence the name from φῦσα, a bladder, and stigma).
The plant is a large, herbaceous, climbing perennial, with the stem woody at the base, up to 2 inches (5 cm) in diameter; it has a habit like the scarlet runner, and attains a height of about 50 feet (15 m). The flowers, resting on axillary peduncles, are large, about an inch long, grouped in pendulous, fascicled racemes pale-pink or purplish, and heavily veined. The seed pods, which contain two or three seeds or beans, are 6 or 7 inches (15 or 18 cm) in length; and the beans are about the size of an ordinary horse bean but much thicker, with a deep chocolate-brown color.
Calabar bean contains physostigmine, a reversible cholinesterase inhibitor alkaloid. The alkaloid physostigmine acts in effect like nerve gas, influencing communication between the nerves and muscles, and resulting in copious salivation, seizures, loss of control over the bladder and bowels, and eventually loss of control over the respiratory system, causing death by asphyxiation.
The main antidote to Calabar bean poisoning is the slightly less toxic tropane alkaloid atropine, which may often succeed; and the other measures are those usually employed to stimulate the circulation and respiration. Unfortunately, the antagonism between physostigmine and atropine is not perfect, and Sir Thomas Richard Fraser has shown that in such cases there comes a time when, if the action of the two drugs is summated, death results sooner than from either alone. Thus atropine will save life if three and a half times the fatal dose of physostigmine has been taken, but will hasten the end if four or more times the fatal dose has been ingested.
...
Wikipedia
