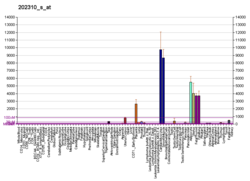
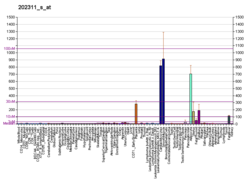
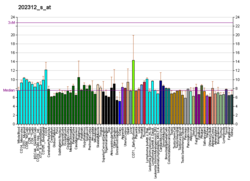
COL1A1
Collagen, type I, alpha 1, also known as alpha-1 type I collagen, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the COL1A1 gene. COL1A1 encodes the major component of type I collagen, the fibrillar collagen found in most connective tissues, including cartilage.
Collagen is a protein that strengthens and supports many tissues in the body, including cartilage, bone, tendon, skin and the white part of the eye (sclera). The COL1A1 gene produces a component of type I collagen, called the pro-alpha1(I) chain. This chain combines with another pro-alpha1(I) chain and also with a pro-alpha2(I) chain (produced by the COL1A2 gene) to make a molecule of type I procollagen. These triple-stranded, rope-like procollagen molecules must be processed by enzymes outside the cell. Once these molecules are processed, they arrange themselves into long, thin fibrils that cross-link to one another in the spaces around cells. The cross-links result in the formation of very strong mature type I collagen fibers. Collagenous function includes rigidity and elasticity.
...
Wikipedia