Bunyaviridae
| Bunyaviridae | |
|---|---|
 |
|
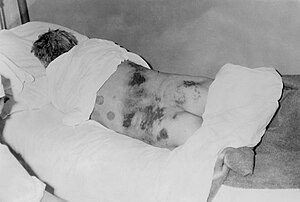
| Isolated male patient diagnosed with Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever (C-CHF) | |
| Virus classification | |
| Group: | Group V ((−)ssRNA) |
| Order: | Unassigned |
| Family: | Bunyaviridae |
| Genus | |
Hantavirus
Nairovirus
Orthobunyavirus
Phlebovirus
Tospovirus
Bunyaviridae is a family of virus belonging to the fifth group of the Baltimore classification, the so called negative-sense single stranded ribonucleic acid (-)ssRNA. They are enveloped RNA viruses. Though generally found in arthropods or rodents, certain viruses in this family occasionally infect humans. Some of them also infect plants.
Bunyaviridae are vector-borne viruses. With the exception of Hantaviruses, all viruses in the Bunyaviridae family are transmitted by arthropods (mosquitos, tick, or sandfly). Hantaviruses are transmitted through contact with deer mice feces. Incidence of infection is closely linked to vector activity, for example, mosquito-borne viruses are more common in the summer.
Human infections with certain Bunyaviridae, such as Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus, are associated with high levels of morbidity and mortality, consequently handling of these viruses must occur with a Biosafety level 4 laboratory. They are also the cause of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome.
Hanta virus or Hantavirus Hemorrhagic fever, common in Korea, Scandinavia, Russia, and western North America, is associated with high fever, lung edema and pulmonary failure. Mortality is around 55%. The antibody reaction plays an important role in decreasing levels of viremia.
Yosemite Outbreak: The Yosemite outbreak lead to the restructuring of preventative measures for park employees. New policies emphasize extensive use of cleaning practices, use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and education of Hantavirus safety training and knowledge of HPS to Yosemite employees. During the time of the outbreak in 2012, the park was required to provide information regarding Hantavirus risks, signs, and symptoms to all tourists who were staying at the camp before September 17th, 2012. Information flyers regarding Hantavirus were posted through the park, and emergency call centers specifically for Hantavirus were required to be accessible and staffed from 9 am to 5 pm.
...
Wikipedia
