Bulbocapnine
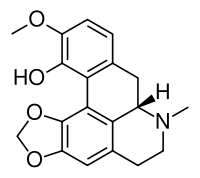 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
(S)-6,7,7a,8-tetrahydro-11-methoxy-7-methyl-5H- benzo[g]-1,3-benzodioxolo-[6,5,4-de]quinolin-2-ol
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
298-45-3 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:3211 |
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL157912 |
| ChemSpider |
11934 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.511 |
| PubChem | 12441 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C19H19NO4 | |
| Molar mass | 325.36 g/mol |
| Melting point | 201 to 203 °C (394 to 397 °F; 474 to 476 K) racemate 213-214 °C |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Bulbocapnine is an alkaloid found in Corydalis (Papaveraceae) and Dicentra, plants in the family Fumariaceae that can cause fatal poisoning in sheep and cattle. It has been shown to act as an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, and inhibits biosynthesis of dopamine via inhibition of the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase.
According to the Dorlands Medical Dictionary, it "inhibits the reflex and motor activities of striated muscle. It has been used in the treatment of muscular tremors and vestibular nystagmus". The psychiatrist Robert Heath carried out experiments on prisoners at the Louisiana State Penitentiary using bulbocapnine to induce stupor. Experiments were used in MKULTRA.
...
Wikipedia
