Brachialis
| Brachialis | |
|---|---|

Deep muscles of the chest and front of the arm, with the boundaries of the axilla. (Brachialis visible at bottom right.)
|
|
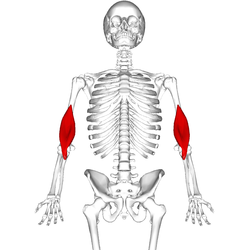
Position of brachialis (shown in red).
|
|
| Details | |
| Origin | anterior surface of the humerus, particularly the distal half of this bone |
| Insertion | coronoid process and the tuberosity of the ulna |
| Artery | radial recurrent artery |
| Nerve | musculocutaneous nerve (C5, C6) |
| Actions | flexion at elbow joint |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus brachialis |
| TA | A04.6.02.018 |
| FMA | 37667 |
|
Anatomical terms of muscle
[]
|
|
The brachialis (brachialis anticus) is a muscle in the upper arm that flexes the elbow joint. It lies deeper than the biceps brachii, and is a synergist that assists the biceps brachii in flexing at the elbow. It makes up part of the floor of the region known as the cubital fossa. The brachialis is the prime mover of elbow flexion. While the biceps brachii appears as a large anterior bulge on the arm and commands considerable interest among body builders, the brachialis underlying it actually generates about 50% more power and is thus the prime mover of elbow flexion.
The brachialis originates from the anterior surface of the distal half of the humerus, near the insertion of the deltoid muscle, which it embraces by two angular processes. Its origin extends below to within 2.5 cm of the margin of the articular surface of the humerus at the elbow joint. Its fibers converge to a thick tendon, which is inserted into the tuberosity of the ulna and the rough depression on the anterior surface of the coronoid process of the ulna.
The muscle is occasionally doubled; additional slips to the supinator, pronator teres, biceps brachii, lacertus fibrosus, or radius are more rarely found. (A "slip" in this context refers to an accessory or variant part of a muscle that has an unusual trajectory in growth relative to the normal fibers' direction of growth.)
The brachialis muscle is innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve, which runs on its superficial surface, between it and the biceps brachii. However in 70-80% of people, the muscle has double innervation with the radial nerve (C5-T1). The divide between the two innervations is at the insertion of the deltoid.
...
Wikipedia
