Boric oxide
![Crystal structure of B2O3 [1]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d9/B2O3powder.JPG/200px-B2O3powder.JPG) |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
boron oxide, diboron trioxide, boron sesquioxide, boric oxide, boria
Boric acid anhydride |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.751 |
| EC Number | 215-125-8 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number | ED7900000 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| B2O3 | |
| Molar mass | 69.6182 g/mol |
| Appearance | white, glassy solid |
| Density | 2.460 g/cm3, liquid; 2.55 g/cm3, trigonal; |
| Melting point | 450 °C (842 °F; 723 K) (trigonal) 510 °C (tetrahedral) |
| Boiling point | 1,860 °C (3,380 °F; 2,130 K) , sublimates at 1500 °C |
| 1.1 g/100mL (10 °C) 3.3 g/100mL (20 °C) 15.7 100 g/100mL (100 °C) |
|
| Solubility | partially soluble in methanol |
| Acidity (pKa) | ~ 4 |
| -39.0·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Thermochemistry | |
| 66.9 J/mol K | |
|
Std molar
entropy (S |
80.8 J/mol K |
|
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH |
-1254 kJ/mol |
|
Gibbs free energy (ΔfG˚)
|
-832 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Irritant |
| Safety data sheet | See: data page |
|
EU classification (DSD) (outdated)
|
Repr. Cat. 2 |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | noncombustible |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
3163 mg/kg (oral, mouse) |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
|
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 15 mg/m3 |
|
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 10 mg/m3 |
|
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
2000 mg/m3 |
| Supplementary data page | |
|
Refractive index (n), Dielectric constant (εr), etc. |
|
|
Thermodynamic
data |
Phase behaviour solid–liquid–gas |
| UV, IR, NMR, MS | |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
2.55 g/cm3, trigonal;
3.11–3.146 g/cm3, monoclinic
Boron trioxide (or diboron trioxide) is one of the oxides of boron. It is a white, glassy solid with the formula B2O3. It is almost always found as the vitreous (amorphous) form; however, it can be crystallized after extensive annealing (that is, under prolonged heat).
Glassy boron oxide (g-B2O3) is thought to be composed of boroxol rings which are six-membered rings composed of alternating 3-coordinate boron and 2-coordinate oxygen. Because of the difficulty of building disordered models at the correct density with a large number of boroxol rings, this view was initially controversial, but such models have recently been constructed and exhibit properties in excellent agreement with experiment. It is now recognized, from experimental and theoretical studies, that the fraction of boron atoms belonging to boroxol rings in glassy B2O3 is somewhere between 0.73 and 0.83, with 0.75 ( 3⁄4) corresponding to a 1:1 ratio between ring and non-ring units.
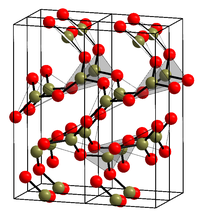
The crystalline form (α-B2O3) (see structure in the infobox) is exclusively composed of BO3 triangles. This trigonal, quartz-like network undergoes a coesite-like transformation to monoclinic β-B2O3 at several gigapascals (9.5 GPa).
Boron trioxide is produced by treating borax with sulfuric acid in a fusion furnace. At temperatures above 750 °C, the molten boron oxide layer separates out from sodium sulfate. It is then decanted, cooled and obtained in 96–97% purity.
Another method is heating boric acid above ~300 °C. Boric acid will initially decompose into water steam and metaboric acid (HBO2) at around 170 °C, and further heating above 300 °C will produce more steam and boron trioxide. The reactions are:
Boric acid goes to anhydrous microcrystalline B2O3 in a heated fluidized bed. Carefully controlled heating rate avoids gumming as water evolves. Molten boron oxide attacks silicates. Internally graphitized tubes via acetylene thermal decomposition are passivated.
...
Wikipedia

